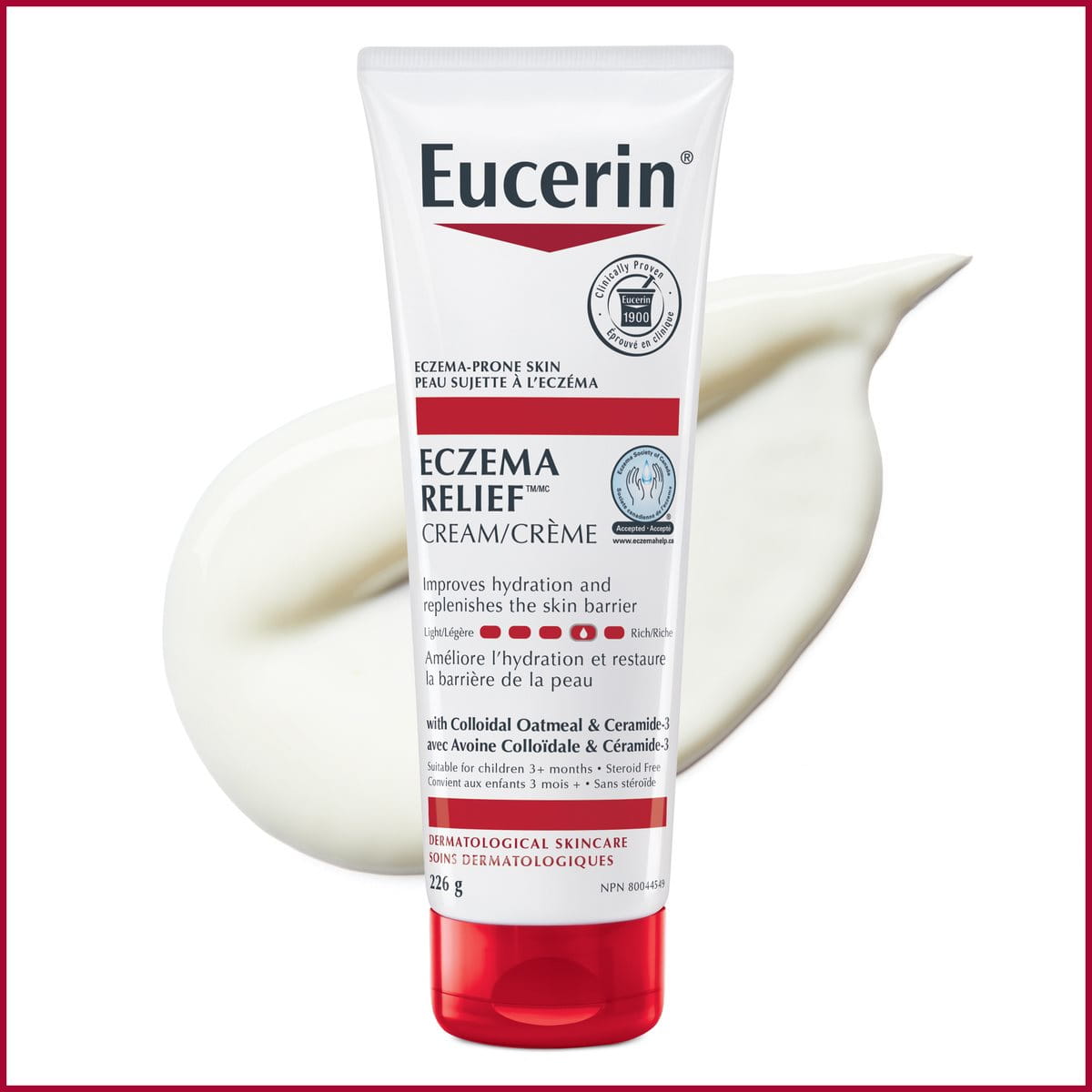
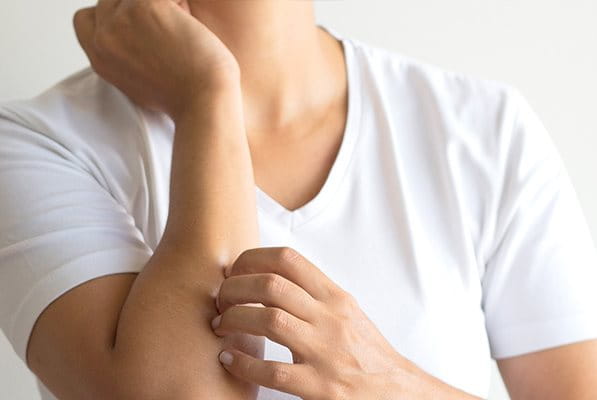
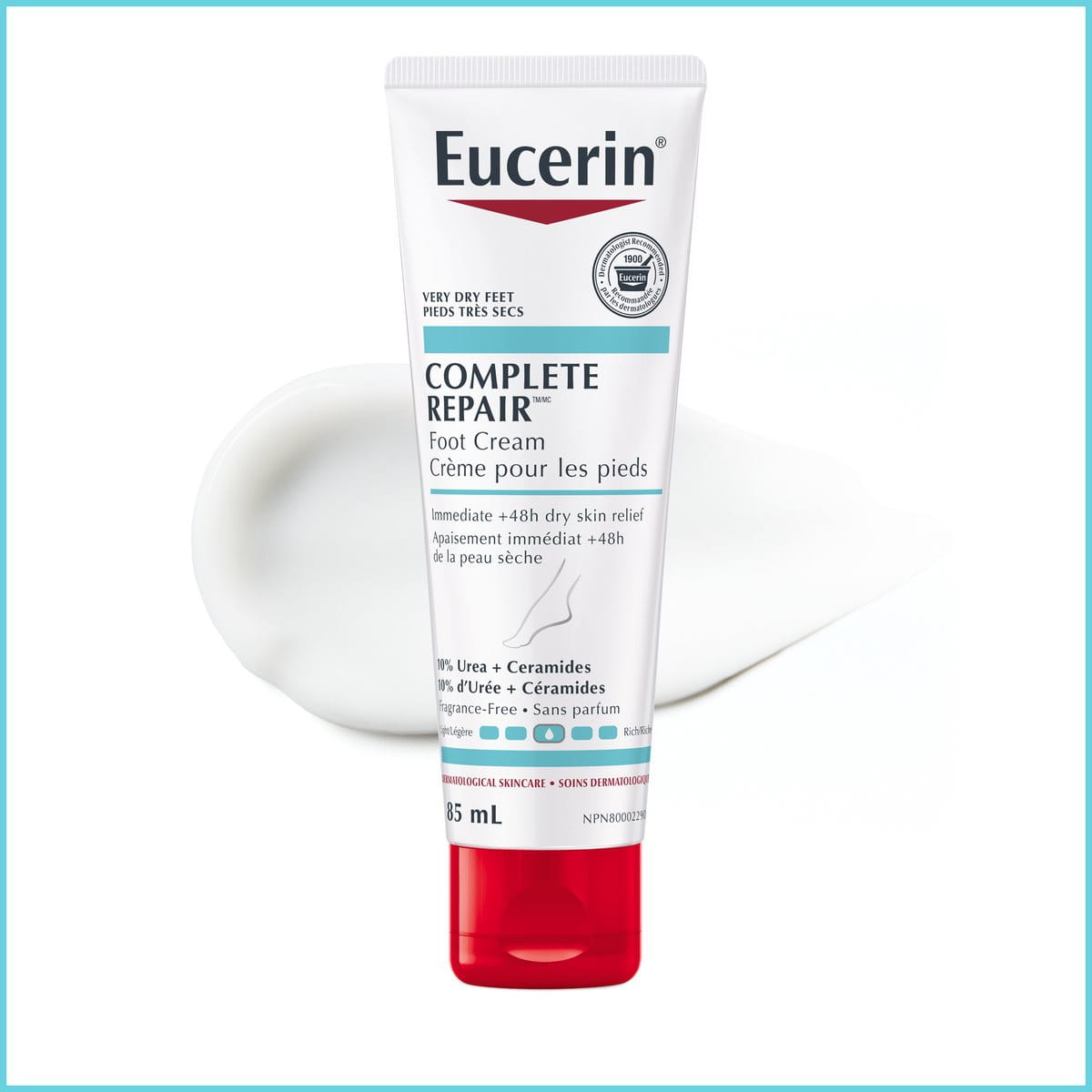
Atopic skin
Manage the active and inactive phases of skin disease to reduce discomfort wherever a flare-up may appear
Filter Articles
Skin Concerns
Body part
Filter Articles